January 26, 2014
Bulk fiber optic cables and patch cords are various types available(Ribbon, tight buffered, breakout, distribution,...), just the jacket material ofbulk fiber optic cablethere is a wide selection.
Plenum Rated Cable
Plenum type is with the highest standard for fire-resistant and it require almost no halogen gas be generated in case it got burned. Complies with NFPA-262 and UL-910. Plenum cables must self extinguish and not reignite. Because plenum cables are routed through air circulation spaces, which contain very few fire barriers, they need to be coated in flame-retardant, low smoke materials. These plastics offer good resistance against possible fire, and in the event that they do begin to burn, they will not emit large quantities of harmful fumes. Plenum cables can be installed in plenums without the use of conduit, meeting specific requirements for flammability and smoke generation.
Riser Rated Cable
Comples with UL-1666. Defined for usage in vertical tray applications such as cable runs between floors through cable risers or in elevator shafts. These spaces cannot be used for environmental air. These cables must self extinguish and must also prvent the flame from traveling up the cable in a vertical burn test. Riser type bulk fiber optic cables are also required to be fire-resistant, but it is not so strict as halogen gas produced if it caught on fire. They are certified for use in riser applications, engineered to prevent the spread of fire from floor to floor in a building.
Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) Rated Cable
Examples of Halogens include Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, and Iodine. LSZH fiber optic jackets are more fire-resistant compared with common PVC jacketed cables, even when they are on fire. When burned,LSZH cableemits low smoke and no halogen substances. This feature is designed to not only protect the environment, but the low smoke is also important to the safety and presence of people and the facilities that could be on fire. These cables will self extinguish but cannot pass UL-910 or UL-1666 for a plenum or riser rating. LSZH cables are used in shipboard applications and computer networking rooms where toxic or acidic smoke and fumes can injure people and/or equipment.
ROHS Rated Cable
RoHS, short form for the Restriction of Hazardous Substances in electrical and electronic equipment. RoHS is made for environmental protection and to protect the health of the products' users. RoHS mentioned six types of hazardous substances: Pb,Cd, Hg, Cr6+, PBDE and PBB.
PVC Cable
PVC means polyvinyl chloride, and it is a common plastic cable insulation or jacket. In a fire, PVC-coated wires can form hydrogen chloride fumes, the chlorine serves to scavenge free radicals and is the source of the material's fireretardance.
After the introduction of cable jacket material above, you may figure out how to choose the type of cable jacke. For fire safety and code compliance concerns, choose Plenum rated cable. If fire safety is not any concern or local code requirement, choose PVC for ease of installation and lower cost.BUY Fiber Optic Ribbon Cable, Riserhere.
Posted by: mikofy at
06:57 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 507 words, total size 4 kb.
January 22, 2014
Ribbon cable is preferred where high fiber counts and small diameter cables are needed. This cable offers the highest packing density, since all the fibers are laid out in rows, typically of 12 fibers, and the ribbons are laid on top of each other. Not only is this the smallest cable for the most number of fibers, it's usually the lowest cost. Typically 144 fibers in ribbons only has a cross section of about 1/4 inch or 6 mm and the jacket is only 13 mm or 1/2 inch diameter! Some cable designs use a "slotted core" with up to 6 of these 144 fiber ribbon assemblies for 864 fibers in one cable! Since it's outside plant cable, it's gel-filled for water blocking or dry water-blocked. Another advantage of ribbon cable is Mass Fusion Splicers can join a ribbon (12 fibers) at once, making installation fast and easy. Ribbon pigtails are spliced onto the cable for quick termination. Premises cabling also uses some ribbon cables, often in preterminated cabling systems where 12 fibers are terminated in one MTP connector. These cables are common in LAN backbones and data centers.
The precise fiber and ribbon geometries result in excellent mass splicing yields. Surrounding the tube are dielectric strength members that provide tensile strength and innovative waterblocking tapes that reduce cable weight and preparation time. This design is also compatible with standard ribbon cable procedures and hardware for easy field installation and reduced labor costs.

A coherent optical fiber bundle in which the configuration is flat rather than round, giving an output in a line. Fiber optic ribbon cable is available bare (without a jacket or Kevlar) and also available with a plenum jacket or Riser jacket. A typical ribbon has 12 color coded fibers and cables can be made with multiple Ribbons. The jackets on ribbon cable are oval and can be broken out into fanout assemblies providing individual single connectors or using a MTP connector for multiple fibers being terminated with one connector.
Ribbon Riser Cables with OFNR rated sheath are intended for indoor premises and riser installations. A UV-resistant, flame-retardant jacket allows added flexibility in placing this cable outdoors, whether it is an aerial, duct or direct-buried application, or indoor general horizontal or riser applications. The cable consists of a ribbon stack of 12-fiber ribbons within a gel-filled central buffer tube. With easily accessible individual 250μm colored fibers, the ribbons have readily identifiable ribbon ID numbers and fiber colors. Utilizing a dry central tube design, the ribbon riser cable proves to be a clean and easy cable for rapid installation, preparation, and splicing. With a high density ribbon design, it is the ideal cable for connecting the vault to the distribution panel, minimizing the use of riser space.BUY Fiber Optic Ribbon Cable, Riserhere. FiberStore not only provide fiber optics, but also there are POF Fiber(Plastic Optic Fiber) available, want to knowPOF Fibermore, just click it.
Posted by: mikofy at
08:23 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 493 words, total size 4 kb.
January 15, 2014
FiberStore is a reliable and trusted supplier of cost-effective SD/HD/3G-SDI video SFP transceiver modules. Our SMPTE MSA SD/HD/3G-SDI video SFP transmitter modules are manufactured with high quality components and tested strictly to ensure the reliability and quality. These HD SD digital video optical transceivers are available in SFP packages and in different configurations.
Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) has standards for handling high definition video signals with pathological pattern. SMPTE’s standards currently call for SMPTE 259M (SD-SDI 270/360Mb/s), SMPTE 292M (HD-SDI 1.485Gb/s), SMPTE 424M (3G-SDI 2.97Gb/s), and SMPTE 424M. SMPTE 424M is a standard which expands upon SMPTE 259M, SMPTE 344M and SMPTE 292M, allowing for bit-rates of 2.970 Gbit/s and 2.970/1.001 Gbit/s over a single link cable.
Features
Robust error free transmission of signals from 50Mbps to 3Gbps with up to 80km single-mode fiber.
MSA pin arrangement.
Supports video pathological patterns for SD-SDI, HD-SDI and 3G-SDI
Hot-pluggable, low Power Consumption.
Diagnose and control via I2C interface including:
Monitoring of laser bias current, average output power, receive optical power, supply voltage and temperature.
RoHS compliant and Telcordia GR-468 compliant.
Video Transceiver like Video CWDM SFP/ Video Single-mode SFP / Video
Multimode SFP / Video APD Receiver / Video BiDi SFP / video DWDM SFP
available.
Applications
SMPTE 297-2006 compatible optical-to-electrical interfaces
HD Video Broadcast cameras
High-density video routers
Fiber-Optic Video Transmission System
Advantages Of Video SFP Module
a. The Video pluggable SFP can meet high quality video signal transmission requirements over long distances.
b. The Video SFP transmitter also provides an optional Digital Diagnostic functions to monitor extensive output optical power, bias current, supply voltage and operating temperature.
c. Video SFP allows
uncompressed digital video component signal transport over any standard
optical transport system, allows standard optical transceivers (MSA
compliance), supports digital video links over fiber optic cabling.

FiberStore SFP-3G31-2D-XX video SFP module is high performance, cost
effective single channel 3G HD, transmits optical signals at 1310nm
wavelength with up to 2km single mode optical fiber (SMF), designed to
transmit optical serial digital signals as defined in SMPTE 297-2006.
The single channel 3G HD video SFP transceiver modules are specifically
designed for robust performance in the presence of SDI pathological
patterns for SMPTE 259M, SMPTE 344M, SMPTE 292M and SMPTE 424M serial
rates. They are compatible with SFP Multi-Source Agreement (MSA) and
SFF-8472.
As a major fiber optic transceiver manufacturer, FiberStore also supplies other transceivers such as multi mode SFP, compatible SFP, SFP+, XFP, X2, XENPAK, 40G QSFP+, 40G & 100G CFP, direct attach cables and so on.
Posted by: mikofy at
08:42 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 426 words, total size 4 kb.
January 08, 2014
Fiber cable termination is the addition of connectors to each optical fiber in a cable. The fibers need to have connectors fitted before they attach to other devices. Two common solutions for fiber cable termination are pigtails and fanout kits or breakout kits.
For doing fiber termination, using fiber termination tools is helpful and save you a lot time. Common fiber termination tools include cable jacket stripper, connector crimper, fiber scriber or cleaver, kevlar cutter, polish film, wipe paper, fiber optic polishing paper, polishing plate (glass or plastic), Fusion splicer and appropriate strippers and cleavers, etc.
Fusion splicing of factory preterminated pigtails. Also popular with telcos, long-distance carriers, and the military, this type of termination method offers performance that is as good as a factory preterminated connector with very low back reflection. Again, this termination method requires an expensive fusion splicer, and connector costs are at a mid-price point.
Fusion splicing machines have decreased in price and increased in features and quality like many other technologies. Whereas 10 years ago a fusion splicer was big and bulky and cost approximately $25,000, today's units are smaller, lighter and more efficient, and they typically cost $7,000 to $12,000. Although a fusion splicer is still an expensive tool, its cost can be easily justified, providing a return on investment in many high-end or high-volume applications. Same phenomenon comes to the fiber optic tool kit price, with more useful tool and more functions but a lower price.
A fiber optic termination tool can be used for varying purposes. Fiber optic termination tools are ideal for:
Mechanical strippers or chemical solvents are used to strip the buffer
and coating material from fiber before being cleaned with alcohol.
A diamond or metal blade is then used to nick the fiber before tension is applied causing it to break.
The fiber is then polished using grit abrasive paper until the finish is smooth.
The end of the fiber is then inspected with a microscope to insure that the end of the fiber is smooth.
Fibers are then attached to connectors or they are joined together by splicing.
FiberStore provide a complete line of cables, connectors, fiber termination tools, tool kits, and test equipments for installing and testing fiber optic infrastructures, also offer part of our larger, comprehensive line of fiber optic products for long haul transmission. For bulk fiber optic cable, the fiber optic termination kit enable you fast and reliable termination in the field. Fiber optic tool kits from FiberStore are built to accommodate all types of fiber systems and connectors. Whether you are terminating, testing, splicing, inspecting or cleaning fiber optic cabling and networks. Our fiber tool kits feature different fiber kits to handle all aspects of servicing fiber systems from splicing, crimping, stripping and polishing to testing, restoring, inspecting and fiber safety.
Posted by: mikofy at
07:06 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 472 words, total size 4 kb.
January 03, 2014
Today, locating is complex as telecommunications cables join utility lines in the underground environment. The underground cable wire locator relies on the basic technology--injecting an electrical signal onto the
cable being located, to locating a specific circuit breaker,
pinpointing wires before drilling and verifying dig sites underground.
Underground wire finder is the rugged, economical solution for locating
cable, wires and pipes that are underground no matter whether they are
energized or de-energized.

NF-816
A cable locator has two basic components: a hand-held receiver and
compact transformer(or transmitter). Both are battery-powered,
relatively light and housed in weather-resistant cases. The receiver
locates underground lines by detecting magnetic fields created by
electrical current passing through cable or tracer wires. Information is
displayed in a window at the top of the receiving unit.
Anatomy of underground cable locator
There are many types of underground wire finders, but they all functioned according to the same principles. The transmitter sends an electric signal which reaches the underground cables, which is then picked up again by the receiver. These devices can help you map an area before you start any actual work.
The transmitter puts an electrical signal onto the cable or pipe being traced, while the receiver picks up that signal, allowing the locator operator to trace the signal's path and follow the cable being located.
Usually receivers use different frequencies and modes to identify different types of utilities. Frequency choices can range from less than 1 kilohertz to about 480 kHz. With this range of frequencies, it is important to keep one thing in mind, if you want to start out at the lowest frequency and if that frequency works, don't change it, lower frequencies seem to bleed over less and stay on the conductor you are attached to better.
The three most common methods of sending signals onto the cable are direct connect, general induction, and inductive coupling. In the inductive coupling method, the cable must be grounded to form a complete circuit path. The direct-connect method allows you to physically attach your transmitter to the cable to be located. That may mean connecting to a cabinet or a pedestal and then gaining access to the shield that surrounds the cable, which is usually grounded at this point.
If directly attaching to the cable is impossible, then the induction method may be the logical choice. Here, you place the transmitter on the ground directly over the cable. Once the transmitter is turned on, it induces a signal into any nearby conductor within its range. This, of course, can lead to problems if there are multiple cables buried within close proximity because the signal could be picked up on a cable other than the one you are trying to trace.
Although inductive coupling doesn't let the user directly connect to the cable, underground wire finder provides a higher level of confidence than does general induction. It uses a donut-shaped coupling device that surrounds the cable and emits a signal onto the cable.
Posted by: mikofy at
04:28 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 501 words, total size 5 kb.
December 26, 2013
Over several years of 10 gigabit Ethernet's R&D, there have been numerous
different form factors and optics types introduced. The oldest, XENPAKs, still
very popular as the install base is large, while the newest SFP+(or SFP plus)
offers a much smaller form factor and the ability to offer 1G/10G combo ports on
hardware for the first time. Currently XENPAK, X2, XFP and SFP
plus are four standard 10G modules available.

Within
these form factors are many different types of optical and electrical
specifications; the only requirement is that the optics type match. It is
perfectly acceptable to connect an X2 to an SFP, or a XENPAK to an SFP+, or any
other combination.
XFP modules are hot-swappable and protocol-independent. They can operate over a single wavelength or use dense wavelength-division multiplexing techniques, signal rates of 10.30 Gb/s to 11.3 Gb/s, typically operate at near-infrared wavelengths of 850nm, 1310nm or 1550nm. Common applications include 10 Gigabit Ethernet, 10 Gbit/s Fiber Channel, synchronous optical networking (SONET) at OC-192 rates, synchronous optical networking STM-64, 10 Gbit/s Optical Transport Network (OTN) OTU-2, and parallel optics links. They include digital diagnostics that provide management that were added to the SFF-8472 standard. XFP modules use a LC fiber connector type to achieve high density.
XFP-SR
XFP-SR is 10Gbps fiber optic transceiver working
at 850nm wavelength, typical working distance of 300 meters. XFP-SR is suitable
for use in 10G datacom (belly-to-belly for high density applications) and
storage area network (SAN/NAS) applications based on IEEE 802.3ae and Fiber
Channel standards.
XFP-LR
XFP-LR is hot swappable fiber optic transceiver
used for 10G networks like 10 Gigabit Ethernet, SDH, SONET. XFP-LR supports data
transfer rate from 9.95Gbps to 11.1Gbps, with a max working distance of
10km.
XFP-ER
XFP-ER adopts cooled EML laser diode and PIN
photodiode, fully compatible with XFP MSA and IEEE 802.3ae-2002, max working
span of 40km.
XFP-ZR
XFP-ZR is 10Gbps fiber optic transceiver which is
compatible with IEEE 802.3ae and Fiber Channel standards. XFP-ZR uses single
mode optical fiber and its max working span can reach to 80km, working
wavelength of 1550nm.
FiberStore provide high quality & cost effective 10G XFP transceiver moudles, including 10GBASE-SR for 300m with OM3 grade multimode fiber, 10GBASE-LR for 10km-20km, 10GBASE-ER for 40km and 10GBASE-ZR for 80km. All modules can support Digital Optical Monitoring (DOM) function. Compatible XFP transceiver modules like Cisco XFP, Juniper XFP, Brocade XFP, Dell XFP, 3Com XFP, Foundry XFP, Extreme XFP, Alcatel-Lucent XFP, Force10 XFP 10Gb, etc. are also available. Buying compatible Force10 XFP (for example) module is a cost-effective way, rather than buying an expensive original Force10 XFP transceiver.
Posted by: mikofy at
08:15 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 436 words, total size 4 kb.
September 17, 2013
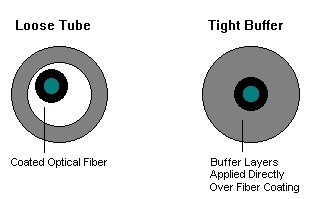
You may familiar with bulk fiber optic cables, but how much do you know the differences betweentight buffer fiberand loose tube cable?
Tight buffer or tight tube cable designs are typically used for ISP applications. Each fiber is coated with a buffer coating, usually with an outside diameter of 900m.
Loose buffer or loose tube cables mean that the fibers are placed loosely within a plastic tube whose inner diameter considerably larger than the fiber itself. Usually 6 to 12 fibers are placed within a single tube. The interior of the plastic tube is usually filled with a gel material that protects the fibers from moisture and physical stresses that may be experienced by the overall cable. Loose buffer designs are used for OSP applications such as underground installations, lashed or self-supporting aerial installations, and other OSP applications.
2. Each Construction Has Inherent Advantages
Each construction has inherent advantages. The loose buffer tube offers lower cable attenuation from microbending in any given fiber, plus a high level of isolation from external forces. Under continuous mechanical stress, the loose tube permits more stable transmission characteristics. The tight buffer construction permits smaller, lighter weight designs for similar fiber configuration, and generally yields a more flexible, crush resistant cable.
The other fiber protection technique, tight buffer, uses a direct extrusion of plastic over the basic fiber coating. Tight buffer constructions are able to withstand much greater crush and impact forces without fiber breakage.
The tight buffer design, however, results in lower isolation for the fiber from the stresses of temperature variation. While relatively more flexible than loose buffer, if the tight buffer is deployed with sharp bends or twists, optical losses are likely to exceed nominal specifications due to microbending.
3. Tensile Loading
Cable tensile load ratings, also called cable pulling tensions or pulling forces, are specified under short-term and long-term conditions. The short-term condition represents a cable during installation and it is not recommended that this tension be exceeded. The long-term condition represents an installed cable subjected to a permanent load for the life of the cable. Typical loose-tube cable designs have a short-term (during installation) tensile rating of 600 pounds (2700 N) and a long-term (post installation) tensile rating of 200 pounds (890 N).
Nowadays there are many big brands fiber optic cable manufacturers available, for example, Corning, who specializes in cables for many years. Thecorning fiber optic cableis of many types and with high quality. Another famous manufacturer--FiberStore, also offers a wide range of bulk fiber optic cables, including cables from corning and cables for different applications,bulk fiber optic cablecan be made in a variety of lengths and configurations to meet your needs.
Posted by: mikofy at
03:06 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 453 words, total size 4 kb.
September 13, 2013
In general, fiber optics cost from 1 to 5 percent more than standard copper wire and multimode fiber sells at a higher price than single-mode fiber.
Although single-mode fiber is by far the predominant fiber for telecommunications, multimode is used in short-reach applications, including for data centers and some other local area networking deployments, as well as for numerous specialized applications not for telecom, such as medical uses, imaging and some illumination.
Multimode is not cheaper than single-mode fiber. However, the inexpensive LEDs or vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) and detectors used to power it are generally less expensive than its single-mode fiber counterparts. The real growth potential is in data centers using VCSELs with multimode fiber. Optical component vendors that can use VCSELs to carry signals in duplex or multistrand multimode fibers may find a market in local area networks or the growing number of data centers throughout the world. Short-range links would appear to be perfect for multimode fibers.
Although konw multimode fiber is more expensive than single mode fiber, what are the other factors deciding the fiber optic cable price?
Fiber optic cable prices are different based on the different cable types, even for the same structure fiber optic cables, the prices may be different because of the different fiber counts, jackettypes, lengths, etc.
The cable design influences the cost of a fiber optic cable. A simple duct cable will be less priced than a direct buried cable, which needs extra protection to meet additional mechanical and environmental safety when the cable is used for direct buried application. A self-supporting type aerial cable may be more expensive than a duct and direct buried type cables. The number of sheaths affects the cost. The more the number of sheathing layers, the higher the cost of cable will be. Process cost and material cost increases drastically proportional to the number of sheathing layers.
It is not always the construction of a cable that decides the cost of a fiber optic cable. The quantity required and delivery also plays major role in the costing of a fiber optic cable. A more quantity, cable manufacturers will offer a cheaper price. When buying a fiber optic cable from fiber optic cable manufacturer, most probably if we approach a cable manufacturer with a requirement of fiber optic cable, they will ask the quantity and delivery time at first apart from the construction requirements.
Fiber optic cable prices from differentfiber optic cable manufacturersare also not same, sometimes they may be quite different, even you are asking about the same structure cable, this may be because of the quality, but brand names may also affect the fiber cable prices.
As you know, Corning developed the first commercial optical fiber in 1970. Corning and OFS remain the No. 1 and No. 2 fiber optic cable makers in the world currently. Corning and OFS almost control every aspect of the optical fiber-making process, including extruding the glass from draw towers, doping it, cooling it, stringing it, testing it, marking it, and then either cabling it or shipping it to other cablers.
Another hidden factor influencesfiber optic cable priceis the market. If the demand is more and competitors are less, the price will be naturally higher.
Posted by: mikofy at
07:21 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 544 words, total size 4 kb.
September 12, 2013
You hear about fiber optic cables whenever people talk about telephone system, cable TV system or the Internet. They are also used in medical imaging and mechanical engineering inspection nowadays. How much do you know the basic information of cables? For example, what a 9/125/250µm cable mean. In this article, we will show you some cable basics.
Cable Size
The size of the optical fiber is commonly referred to by the outer diameter of its core, cladding and coating. Example: 50/125/250µm indicates a fiber with a core of 50 microns, cladding of 125 microns, and a coating of 250 microns. The coating is always removed when joining or connecting fibers. A micron (µm) is equal to one-millionth of a meter. 25 microns are equal to 0.0025 cm. (A sheet of paper is approximately 25 microns thick).
Cable Types
Cables can be identified by the type of paths that the light rays, or modes, travel within the fiber core. Also according used in different environments, there are outdoor cable,waterproof cables, lszh cable, submarine optical cable, etc.
Distribution Cables
These cables are small in size, and used for short, dry conduit runs, riser and plenum applications. The fibers are double buffered and can be directly terminated, but because their fibers are not individually reinforced, these cables need to be broken out with a "breakout box" or terminated inside a patch panel or junction box.
Breakout Cables
They are suitable for conduit runs, riser and plenum applications. Because each fiber is individually reinforced, this design allows for quick termination to connectors and does not require patch panels or boxes. Breakout cable can be more economical where fiber count isn't too large and distances too long, because is requires so much less labor to terminate.
Loose Tube Cables
These cables are composed of several fibers together inside a small plastic tube, which are in turn wound around a central strength member and jacketed, providing a small, high fiber count cable. This type of cable is ideal for outside temperatures and high moisture conditions(waterproof cables also do good jod in moisture conditions), as it made with the loose tubes filled with gel or water absorbent powder to prevent harm to the fibers from water. It can be used in conduits, strung overhead or buried directly into the ground.
Ribbon Cable
This cable offers the highest packing density, since all the fibers are laid out in rows, typically of 12 fibers, and laid on top of each other. This way 144 fibers only has a cross section of about 1/4 inch or 6mm! Some cable designs use a "slotted core" with up to 6 of these 144 fiber ribbon assemblies for 864 fibers in one cable! Since it's outside plant cable, it's gel-filled for water blocking.
Armored Cable
Used for rodent protection in direct burial if required. This cable is non-gel filled and can also be used in aerial applications. The armor can be removed leaving the inner cable suitable for any indoor/outdoor use. (Temperature rating -40ºC to +85ºC)
Indoor/Outdoor Cable
Indoor/Outdoor cables combine the flame resistance and safety features of an indoor riser or plenum cable with the durability that is critical for OSP use. The result is a unique, dual-purpose cable that can save time and money by allowing OSP applications to flow seamlessly indoors, using a single cable and no splices.
Aerial Cable
Aerial cables are for outside installation on poles. They can be lashed to a messenger or another cable (common in CATV) or have metal or aramid strength members to make them self supporting.
Special Cable
These cables combine specialty optical fiber with cabling construction that make installation or deployment easier and/or protect the fibers for long-term use in harsh environments.
Even more types of cables are available and also many brands cables from different manufacturers are available. Corning is one of the outstandingfiber optic cable manufacturers, who invented the first commercially viable low-loss optical fiber in 1970. Today Corning remains the global market leader in the industry, thecorning fiber optic cableis recognized for their excellence and innovation.
Posted by: mikofy at
03:51 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 681 words, total size 5 kb.
September 11, 2013
Fiber optic cables are common in today's telecommunication, but how much do you know their design.
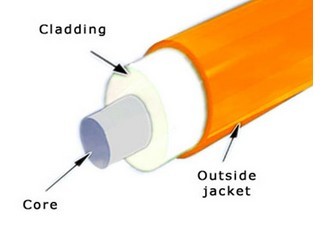
From the fiber production process, the composition of the fiber from the inside out: the core, cladding, a coating, and secondary coating. Thebare optical fibermeans it has not been coated, only with fiber optic core and cladding. Optical signals in optical fibers are using light of the principle of total reflection. The glass fiber is the main channel of transmission of optical signals, the cladding is used to reflect the optical signal, and the coating is to protect the fragile core.
Bare glass fibers are based on silica or other glass materials. The glass surface is susceptible to abrasion and mechanical flaws. To protect the cable from the environment, the buffer coating or jacket fits over the core and cladding. The diameter ranges from 250μm to 900μm, usually 250um for single mode and multimode fibers, but 400um is also very common in polarization maintaining fibers. It provides mechanical protection while allowing for flexibility in the fiber. The buffer coating is usually made of a soft or hard plastic such as acrylic or nylon. Kevlar is a popular choice for the jacket material. It is strong and used to bundle and protect the loose tubes or fibers in the cable. Kevlar protects the fibers when the tension is placed on the cable. The color of this jacket typically depends on the type of fiber, single mode fibers typically wear a yellow jacket and multi-mode fibers wear an orange jacket.
A secondary buffer coating is then applied to the fibers to give protection against external mechanical and environmental factors. This layer may take different designs and its main function is to prevent micro-bending losses.
A. 900um tight buffer. A 900um diameter hard plastic material is coated as the secondary buffer layer. The material is usually Nylon, Hytrel or Tefzel and it provides stiffening for the fiber against outside microbending influences. With tight buffered single mode or multimode optical fiber secondary coating structure is namedtight buffered cable. It is the basic components for the manufacture of a variety of indoor cable, which can also be used alone. The tight buffer fiber can be used directly in pigtail for the connection of various types of optical active or passive components, instruments and terminal equipment connections.
B. Loose tube. Another alternative approach to a direct tight buffer coating is to use a 900um loose tube. The 250um or 400um bare fiber is placed in an oversized loose tube in which the fiber is mechanically isolated from external forces. Then, coupled with strengthening the core which used to increase the fiber optic cable strength and the outer sheath, such as aluminum foil and polyethylene jacket, became a fiber optic cable.
C. Filled loose tube. The loose tube discussed above can be filled with moisture-resistant compound which provides mechanical protection and a water barrier layer around the fiber. This filling material is generally petroleum or silicone-based compounds.
There are many types fiber optics from variousfiber optic cable manufacturersand you can have a look at FiberStore, who is professional in cables.
Posted by: mikofy at
04:24 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 524 words, total size 4 kb.
September 06, 2013
Fiber optic cables are widely used in modern, gradually replace of copper cables.
Key Specifications Of Fiber Optic Cables
·Transmission rate of 100 Mbps;
·Cable length of 2 kilometers or more;
·Not affected by electrical interference;
·Supports voice, video, and data;
·Provides the most secure media;
·Commonly used in backbones between buildings and Token Ring networks;
·Specifications for fiber include the IEEE's 10BaseFL (Ethernet) and ANSI's FDDI or Fiber Distributed Data Interface (Token Ring).
Depending on the number of fibers and how and where it will be installed, bulk fiber optic cables come in lots of different types. Choose cable carefully as the choice will affect how easy it is to install, splice or terminate and, most important, what it will cost! Such astight buffered fiber cableand loose tube cable. Loose tube cable majority used in outside-plant installations, while tight-buffered cable primarily used inside buildings.
Tight Buffered Cable
Tight buffered (coated with a 900 micron buffer over the primary buffer coating) with Kevlar (aramid fiber) strength members and jacketed for indoor use. The jacket is usually 3mm (1/8 in.) diameter. Zipcord is simply two of these joined with a thin web. It's used mostly for patch cord and backplane applications.
Single-mode tight-buffered cables are used as pigtails, patch cords or jumpers to terminate loose-tube cables directly into opto-electronic transmitters, receivers and other active and passive components. Multimode tight-buffered cables also are available and are used primarily for alternative routing and handling flexibility and ease within buildings.
Distribution Cables
Distribution Cables contain several tight-buffered fibers bundled under the same jacket with Kevlar strength members and sometimes fiberglass rod reinforcement to stiffen the cable and prevent kinking. These cables are small in size, and used for short, dry conduit runs, riser and plenum applications. The fibers are double buffered and can be directly terminated, but because their fibers are not individually reinforced, these cables need to be broken out with a "breakout box" or terminated inside a patch panel or junction box. They can be multimode distribution indoor cable, single mode plenum distribution indoor cable, multimode plenum distribution indoor cable, waterproof cables, etc.
Loose Tube Cable
In a loose-tube cable design, color-coded plastic buffer tubes house and protect optical fibers. A gel filling compound impedes water penetration. Excess fiber length (relative to buffer tube length) insulates fibers from stresses of installation and environmental loading. Buffer tubes are stranded around a dielectric or steel central member, which serves as an anti-buckling element. The cable core, typically surrounded by aramid yarn, is the primary tensile strength member. The outer polyethylene jacket is extruded over the core. If armoring is required, a corrugated steel tape is formed around a single jacketed cable with an additional jacket extruded over the armor.
FiberStore covers a wide production line ofbulk fiber optic cable, from common bare fiber,waterproof cablesto special fiber cables for specific applications. Flexible or rigid cables of copper or aluminium, with a complete range of polymers and protectors, always developed under the most stringent international standards.
Posted by: mikofy at
10:06 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 506 words, total size 4 kb.
May 30, 2013
Media Converter Chassis is really predominantly useful to manage all sorts of media converters, along with most of the converters connected to any chassis could publish same exact power. Any fiber media converter chassis will create a lot of media converters utilizing ability, this would effortless any links and structure, it'll job stably and adapt broad width of voltage. It'll retail store good ability and may also get powered together with monitored conveniently. And any maintenance of this chassis is straightforward.
FiberStore has two kinds of rack-mounted fiber optic media converter chassis for unmanaged media converters : 2-U 14 slots media converter chassis and 2-U 16 slots media converter chassis .The 14 slots fiber optic media converter chassis supports plug-and-play installing of stand-alone media converters convert modules ,can hold at most 14 pieces media converters. The 16 slots fiber optic media converter chassis should be combined with card-type media converters .The 16 slots media converter chassis holds at most 16 card-type converters of 10/100M.
Installing in the center of network, the 14 Slot Fiber Optic Media Converter Chassis Rack not only reduce the links, simplify the structure, but also ease for management and maintenance.
14 Slot Fiber Optic Media Converter Chassis Main features: The power of the Rack could be given by the kind of single power or dual power. Adopting dual power supply, the load of every power could be reduced and the life of the power would extend; When one power supply is at fault, the other one can still work independently. It would boost the toughness for the RACK; Supplying the Converters or Powers to become plugged and played; It is possessed of stable performance, large capacity of power supply, and ease for management and maintenance; 2U high: 19-inch standard design.
Media converter chassis is acceptable which are more 16 teams of different Media Converter Cards inside a rack-mountable chassis which is provided with unified power. Installing in the center of network, it can not only reduce the links, simplify the dwelling, but additionally ease for management and maintenance. It can be tidily placed at any network environment. The external type of RACK is straightforward and tidy. It's ready for 10/100Mbps, 10/100/1000Mbps Converter Card to become plugged in, and will also be the best solution of network connections for the continuous growth and development of network.
Media converters transparently connect one sort of media, or cabling, to a different- typically copper to fiber. Obtainable in stand-alone, modular chassis-based, or PCI powered configurations, FiberStore's media converters offer copper to fiber and fiber to fiber media conversion in the following supported protocols: Ethernet Media Converter, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, Power-over-Ethernet, 100/100, 10/100/1000, ATM, T1/E1, DS3/E3, POTS, RS232 to Ethernet, RS485 and more. By bridging the space between legacy copper infrastructures and fiber growth, our media converters provide an economical path towards extending the length of an existing network, extending the life span of non-fiber based equipment, or extending the length between two like devices.
Source from Common 14 Slots And 16 Slots Media Converter Rack Chassis
Posted by: mikofy at
08:35 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 512 words, total size 4 kb.
May 29, 2013
PDH Multiplexer, or Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy multiplexer, is a kind of point-to-point optical transmission equipment used to transport large quantities of data over digital transport media, for example fiber-optic and microwave radio systems. PDH Multiplexer is designed of highly integrated structure and provides 16 standard E1 interfaces together with one channel of order wire, with self-contained alarm and NM functions, in addition to self-testing and E1 loop-back testing functions. The unit is popularly with telecommunication operator. It is suitable running a business for communication operator, government and kinds of entities.
PDH was created in the early 1960s. It derives its names in the Greek term "plesio," meaning near, and "chronos," meaning time. The name refers back to the fact that networks using PDH run in a state of just about, although not quite, perfect synchronization. PDH was the very first standardized multiplexing hierarchy based on time-division multiplexing. It works by channeling numerous individual channels into higher-level channels.
Work Theory Of PDH Multiplexer
The PDH product is in line with the theory when you've two identical
clocks, each the same brand, style and everything, there is no guarantee
that they'll run at the exact same speed. Most likely one of these is
going to be slightly out of synchronization using the other. The
transmitting multiplexer combines the incoming data streams, compensates
for just about any slower incoming information, reconstructs the
initial data and sends it back out at the correct rates. This system
allows for that slight variation in speed and corrects it during
transfer to keep the machine constantly running without pausing and
waiting for certain slower data to arrive before sending it on. PDH
simply fills within the missing bits to match a smooth change in data.
PDH made little provision for management of the network, and the need to fully de-multiplex a high level carrier to extract a lower level signal resulted in enhancing the capacity of PDH networks beyond a certain point wasn't economically viable. The main economic factor was the cost of the equipment required at each cross-connect point within the network where either individual channels or low-level multiplexed data streams should be extracted or added. Additionally, it added additional latency and increased the possibility of errors occurring, thereby reducing network reliability.
Available Kinds of PDH multiplexer
Traditionally, each channel in PDH was a digitized voice, but video
information and knowledge can also be sent of these channels. The
fundamental channel is 64 Kbits per second, which is the bandwidth that
is required to deliver a voice call that's been converted from analog to
digital.
N*E1 PDH Fiber Optic Multiplexers make use of the PDH fiber transmission technologies. The 2M (E1) interfaces can interact with the exchanger, light loop tool and multi-diplexer directly to form the micromini or the special network. Complete alarm function for N*E1 PDH Fiber Optic Multiplexers, it's stable, easy to maintenance and install, small in size. It can support one digital service telephone.
PDH Multiplexer can multiplex 4/8/16E1, Ethernet Media Converter (2*10/100Mbps) and V.35 signals in one fiber channel to deliver. It's ideal for low capacity, point-to-point application of remote transmission. The PDH Multiplexer can be applied to create economical and flexible multi-service transmission networks, employed for relay between switch offices, data transmission of LAN, 2M access of lease service for key clients, voice cutover for residental areas/intelligent buildings, and connection of base stations and other various digital transmission networks. Fiber Optic Multiplexer is reliable, stable, simple to install and keep, which may be monitored from Fi-view-MST management software, that is popular in voice and knowledge application field.
Source from PDH Optical Multiplexer Wiki
Posted by: mikofy at
08:00 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 606 words, total size 5 kb.
May 28, 2013
PON ( Passive Optical Network) refers to the optical distribution network doesn't contain any digital camera and electronic power, optical distribution network (ODN) all by the optical splitter and other passive components, without the need for expensive electronic equipment, is really a type of fiber-optic access network. PON cuts down on the amount of fiber and central office equipment required compared with point-to-point architectures.
A PON consists of an optical line terminal (OLT) at the service provider's central office and a quantity of optical network units (ONUs) near end users. In OLT/ONU between the optical distribution network includes optical fiber and passive optical splitter or Fiber Optic Coupler.
OLT
An OLT, generally an Ethernet switch, router, or multimedia conversion
platform, is located in the central office (CO) like a core device from
the whole EPON system to provide core data and video-to-telephone
network interfaces for EPON and also the company.
ONU
ONUs are
utilized to connect the client premise equipment, for example PCs,
set-top boxes (STBs), and switches. Generally placed at customer's home,
corridors, or roadsides, ONUs are mainly accountable for forwarding
uplink data sent by customer premise equipment (from ONU to OLT) and
selectively receiving downlink broadcasts forwarded by OLTs (from OLT to
ONU).
ODN
An ODN includes optical fibers, a number of passive
optical splitters (POSs), and other passive optical components. ODNs
provide optical signal transmission paths between OLTs and ONUs. A POS
can couple uplink data right into a single bit of fiber and distribute
downlink data to respective ONUs.
There are two passive optical network technologies: Ethernet PON (EPON) and gigabit PON (GPON). EPON and GPON are used in different situations, and every offers its very own advantages in subscriber access networks. EPON concentrates on FTTH applications while GPON concentrates on full service support, including both new services and existing traditional services for example ATM and TDM.
EPON is really a Passive Optical Network which carries Ethernet frames encapsulated in 802.3 standards. It is a mixture of the Ethernet technology and also the PON technology in compliance using the IEEE 802.3ah standards issued in June, 2004. A typical EPON system consists of three components: EPON OLT, EPON ONU and EPON ODN. It has many advantages, for example lower operation and maintenance costs, long distances and higher bandwidths.
GPON utilizes point-to-multipoint topology. GPON standard differs from other PON standards for the reason that it achieves higher bandwidth and higher efficiency using larger, variable-length packets. And GPON is generally considered the best candidate for widespread deployments. GPON includes a downstream capacity of 2.488 Gb/s as well as an upstream capacity of 1.244 Gbp/s that's shared among users.
There are also many differences between EPON and GPON. EPON, based on Ethernet technology, is compliant using the IEEE 802.3ah Ethernet in the First Mile standard that's now merged in to the IEEE Standard 802.3-2005. It's a solution for the "first mile" optical access network. GPON, on the other hand, is a vital approach to enable full service access network. Its requirements were set force by the Full Service Access Network (FASN) group, which was later adopted by ITU-T as the G.984.x standards-an addition to ITU-T recommendation, G.983, which details broadband PON (BPON).
Both EPON and GPON are known as international standards. They cover exactly the same network topology methods and FTTx applications, incorporate exactly the same WDM technology, delivering the same wavelength both upstream and downstream together with a third party wavelength. PON technology provides triple-play, Ip address TV (IPTV) and cable television (CATV) video services.
Source from EPON And GPON Of Passive Optical Network
Posted by: mikofy at
10:24 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 599 words, total size 5 kb.
May 27, 2013
Because the improvement of network, it will be vital that you maintain both configuration flexibility and port utilization for equipment deployed in the intersection of legacy copper and newly installed optical networks. Copper SFP (small form factor pluggable) module ensures the SFP form factor have emerged because the best way to optimize port-level flexibility. The maturation of Copper SFP module is playing a vital role in enabling system designers to satisfy these objectives while simplifying their inventory and reducing operating costs.
Copper SFP module utilizes a copper line for linking. The copper transceiver includes transmit and receive two decision points, Radiating portion includes laser circuit and optical maser, Receiving part includes PIN, TIA and Limtiting Amp, completing digital signal transparent O/E, the E/O conversion functions. Typical copper SFP things like Cisco GLC T and SFP GE T, these SFP modules are used in Gigabit networks and they're fully suitable for 1000Base-T. SFP GE T may be the copper SFP which are with extended working temperature and DOM support. And i'll talk about the common widely used 1000BASE-T copper SFP module below.
1000BASE-T 1000Base T SFP module means the little form fiber optic transceiver that complies with 1000Base-T standards. 1000Base T SFP is copper SFP transceivers also it uses category 5 cables for linking and with a really limited working span. 1000Base T SFP is perfect for Gigabit Ethernet and delay pills work under IEEE 802.3 standards.
Specifications of 1000BASE-T copper SFP module: 1.25 gigabyte Ethernet over cat 5-cable; Extended case temperature range; Switch, router to change, router link; High-speed I/O for file severs; compliant while using Gigabit Ethernet and 1000BASE-T standards as specified by IEEE 802, 3-2002 and IEEE 802.3ab; support 1,000 Mbps full duplex data-links with 5-level pulse amplitude modula-tion (PAM) signals; provide standard serial ID information compliant with SFP MSA, which may be accessed with address of A0h via the 2-wire serial CMOS EEPROM protocol; The physical IC may also be accessed via 2-wire serial bus at address Ach; Qualified to satisfy the intent of Bellcore reliability practices; Compliant with SFP MSA specification and SFF-8472 ; Links of narrow, intermediate or long reach with single or Multi-mode fiber; ROHS, CE and FCC certified; DMI feature on request.
FiberStore Technology, a professional fiber optic products supplier, provides the copper SFP module which are made according to IEEE standards, these copper SFP transceivers are suitable to make use of while using equipment and devices that are with copper SFP slots or ports. The copper SFP module offers a flexible and simple approach to be installed into SFP MSA compliant ports at any time with no interruption from the host equipments operation. It enables for seamless integration of fiber with copper LAN connections wherever SFP interface slots are available. Such system is economical, it saves time, offers flexibility and eliminates the requirement of replacing entire devices when the customers have to change or upgrade fiber connections and you'll benefit a great deal from it.
Fiberstore is experienced on fiber optic technologies and merchandise. Learn much more about Cisco SFP 10G and BiDi SFP on FiberStore.com.
Source from Copper SFP Module Among SFP Transceivers
Posted by: mikofy at
08:13 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 529 words, total size 4 kb.
May 24, 2013
A protocol converter, referred to as protocol translator, accustomed to convert standard or proprietary protocol of one device to the protocol ideal for the other device or tools to offer the interoperability, with every protocol based on many factors. It is much like a language translator, translates messages, or data streams, between networks make it possible for both networks to simply interpret the data. Typical types include E1 to Ethernet, V35 to Ethernet and E1 to V35. Variety protocols utilized in different fields like Power Generation, Transmission & Distribution, Oil & Gas, Automaton, Utilities, AMR, and Remote Monitoring applications.
Structure Of Protocol Converter
The general
architecture of the protocol converter includes an internal master
protocol communicating towards the external slave devices and the data
collected is used to update the internal database of the converter. When
the external master requests for data, the internal slave collects data
in the database and send it to the external master.
The end result of the protocol converter is to allow the protocol of 1 machine communicate with the protocol of another, increasing the quantity of machines the network can use. As the penalties normally are slight, conversion in one protocol to another may slow the bond speed, especially if the converted protocol innately has a lower data rate. Most converters possess a database with several protocols, and this database is used to transform the initial protocol to a different format.
Different Protocols Of Protocol Converter
The majority
of networks have many machines using different protocols, and these
protocols dictate the way a machine acts. These protocols are based on
several factors, including data rate, encryption methods, file and
message formats and associated service, because some services
exclusively use one protocol. A protocol converter is given the job of
taking this protocol and changing it to a different one.
Most protocol converter units are programmed to understand a number of different protocols, and these units use an internal database to trace all the protocols. This database will store all of the factors associated with the known protocols, and the database is also tasked with helping this device understand what must be changed to change one protocol to another. Unlike regular databases, which may be manually updated, this database typically is locked from users.
Options that come with Protocol Converter
Protocol converters provide physical conversion between ITU-T G.703
standard E1 interface and standard V.35, RS232, RS422 converter, RS485
converter and 10M/100M Ethernet interface, offering security and
seamless link for communication between different devices with various
interfaces. Protocol supports IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.1 P, 802.1Q (VLAN).
The interface converter transfers data with V.35, RS232, RS485, RS422
output. E1 interface works with ITU-T G.703, G.704 and G.823 supporting
BNC 75Ω/unbalance impedance and RJ45 120Ω/balance impedance with speed
rates range of 64K~2.048Mbps. Single and multi E1 and framed E1 (FE1)
channels; data interface and Ethernet interface; mini rack and 19 inch
rack; 220V, 110V, 48V power supply or both are optional, in addition to
TDM over IP devices.
Protocol converter series may put into action the actual transformation among single E1 protocol port in addition to protocol ports of V.35, V.24, RS232 Ethernet converter or Ethernet within the tranny system; it may be thoroughly utilized in numerous being able to access issues with regard to providers in addition to commercial clients, for instance DDN, ATM, and for that transformation in between router and E1 port, or perhaps the actual occasion exactly where Ethernet tend to be interconnected from divided internet sites through SDH or even additional tranny gear.
A protocol converter usually is helpful. Protocols are software installed on the routers, they're widely used in a number of industries for applications for example building and process automation. Protocol converters also are employed for substation automation, or a system for managing and controlling equipment within an electrical power system.
Source from Brief Introduction Of Protocol Converter
Posted by: mikofy at
08:06 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 652 words, total size 5 kb.
May 23, 2013
Fiber optic adapter or fiber optic coupler is a medium component, designed to connect two fiber optic cables together. A fiber-optic adapter allows fiber-optic cables to be attached to each other singly or in a large network, allowing many devices to communicate at once. Adapters come in versions to connect single fibers together (simplex), two fibers together (duplex), or sometimes four fibers together (quad). Optical adapters are widely uses in light distribution frame(ODF), the optical fiber communications equipment, the measuring appliance and so on.
Fiber Optic Adapter Specifications:
Insertion Loss < 0.20Db;
Durability Operating Temperature: -40 to 80 °C;
Low insertion loss and back reflection loss;
High precision alignment;
Telcordia, ANSI, TIA/EIA, NTT and JIS compliance.
The fiber optic adapters are many types because of the diversity of the connectors. The fiber optic adapters are available in simplex, duplex and quad (for some types like LC and MU) configurations and with FC, SC, ST, LC, MT-RJ, MU, and more types, type MT-RJ is for use with fiber modem applications. According to the fiber connector types that the adapters used to connect there are standard fiber optic adapter and hybrid fiber optic adapter. Besides, there are also bare fiber optic adapter used to connect with the bare optical fibers directly.
Standard Fiber Optic Adapter
Standard fiber optic adapters are simplex, duplex and quad (for some
types like LC and MU) structures, they are female to female type, used
to link fiber optic connectors, typically they are with ceramic sleeves,
fit for both single mode and multimode fiber optic connections.
Hybrid Fiber Optic Adapter
Fiber optic adapters are typically connecting cables with similiar
connectors (SC to SC, LC to LC, etc.). Some adapters, called "hybrid",
accept different types of connectors (ST to SC, LC to SC, etc.). A
hybrid connector can be designed to fit any two types of fiber-optic
cables together. When the connectors have differing ferrule sizes
(1.25mm to 2.5mm), as found in LC to SC adapters, the adapters are
significantly more expensive because of a more complicated
design/manufacturing process.
Fiber optic adapter are used in fiber optic connection, the typical use is to provide a cable to cable fiber connection. Connecting two cables together can allow two devices to communicate from a distance through a direct connection with the fiber-optic line. These simple types of adapters are often referred to as mating sleeves because they allow two cables to connect to one another. Some of these common line to line connectors are also built to connect three or four cables together.
Fiber optic connectors are available in many different models. Each model works with a specific type of fiber optic cable. This makes it even more important for the user to be sure of the type of fiber optic cable he/she is working with in order to make a compatible connection. Fiber optic cables must also be installed properly to ensure that fiber optic cores line up with each other and allow light to pass through them.
Fiberstore offers a wide selection of connector adapter, including FC, SC, ST, LC, MT-RJ, MU, simplex, E2000, FC/APC,duplex, SC/APC, LC/APC, E2000/APC ,quad, mating sleeves, hybrid fiber optic adapters, single mode fiber optic adapters and multimode fiber optic adapters.
Source from Fiber Optic Connector Adapter As My Know
Posted by: mikofy at
08:14 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 551 words, total size 4 kb.
May 22, 2013
Fiber optical module is seen as a three sets of performance criteria: transceiver, receiver, and transmitter. The transmitter converts electrical signals into light signals, with the fiber optical transmission, the receiving end of the optical signals are changed into electric signals.
According to the optical module function, fiber optic transceivers could be split into fiber optical receiver module, fiber optical transmission module, fiber optical transceiver module and fiber optical transponder module.
Fiber optic transceiver module main function would be to achieve the conversion between optical-electrical and electrical-optical, including optical power control, modulation transmission, signal detection, IV conversion and limiting amplifier decision regeneration, additionally, there are security information query, TX-disable along with other functions. Common fiber optic transceiver modules are: SFP, SFF, SFP , GBIC, XFP, 1x9 and so on.
Fiber optical transmission module not just has photoelectric conversion function, but additionally it integrates lots of signal processing functions, for example: MUX / DEMUX, CDR, function control, energy acquisition and monitoring. Common fiber optical transmission modules: 200/300pin, XENPAK, and X2/XPAK the like.
The optical transceiver module, referred to as optical module or fiber optic module, is an important device in fiber optical communication system.
According to the main parameters of fiber optical module
Pluggable: hot pluggable and non-hot pluggable;
Package: SFP, GBIC, XFP, Xenpak, X2, 1X9, SFF, 200/3000pin, XPAK
Transmission Rate: Transmission rate refers to the quantity of gigabits transmitted per second, per unit of Mb/s or Gb/s. Optical modules cover the following main rate: low rates, Fast, Gigabit, 2.5G, 4.25G, 4.9G, 6G, 8G, 10G and 40G.
According to the optical module package
1.XFP (10 Gigabit Small Form Factor Pluggable) is a hot pluggable transceiver, is independent communication protocol optical transceiver for 10G bps Ethernet, SONET / SDH and Fiber Channel.
2.SFP transceivers (small form factor pluggable), currently are the most favored.
3.GigacBiDi series of single-mode bidirectional optical module, uses WDM technology, achieving a fiber optic transmits two-way information (indicate point transmission, especially for fiber optic resources are insufficient, need a fiber bi-directional signal transmission). GigacBiDi series include SFP Bidirectional (BiDi), GBIC Bidirectional (BiDi), SFP Bidirectional (BiDi), XFP Bidirectional (BiDi), SFF Bidirectional (BiDi) and so on.
4.RJ45 transceiver is electrical port small form factor pluggable module, also referred to as the ability module or electrical interface module.
5.SFF According to their pin, SFF transceivers are divided into 2x5, 2x10, etc.
6 Gigabit Ethernet Interface Converter (GBIC) module.
7 Passive Optical Network PON (A-PON, G-PON, EPON OLT) optical module.
8.40Gbs high-speed optical modules.
9.SDH transmission module (OC3, OC12, OC4![]() .
.
10 Storage modules, such as 4G, 8G, etc.
Source from Classifications Of Fiber Optic Modules
Posted by: mikofy at
07:48 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 438 words, total size 4 kb.
May 21, 2013
Ethernet to serial converter allows large quantities of knowledge to become transferred through each serial port coupled with a quick Ethernet connection. The elevated control and automation of serial over ethernet converter, through your existing network infrastructure, can help you reduce your costs and improve efficiency, yet smart enough for just about any office environment.
Key Features Of Ethernet To Serial Converter:
Cable replacement using serial-Ethernet;
Have virtual COM ports connect PC/servers to remote serial devices over Ethernet;
Communicate to multiple serial devices at the same time across a network;
Use serial-Ethernet to exchange existing serial dial-up modem connections;
Manage the serial console port on remote equipment (Servers, routers,
switches, etc) over Ethernet or through of band connections;
Use serial-Ethernet to connect serial PLCs to Ethernet;
Connect serial signage equipment over Ethernet with serial-Ethernet adapters.
All serial converters feature a minimum of an Ethernet port and software-selectable RS232/422/485 serial interfaces, and meet IEC safety (IEC 60950-1) and EMC (EN 61000) standards. They support various protocols for serial data transmission including Modbus/TCP, raw serial data over UTP, IPv4 and IPv6. The 4 and 8 port RS422/485 devices, as with the rest of the range, will enable connection across a network with no loss of reliability or signal integrity. The Port3 connector signal level is of RS485 or RS232. This port could be stated as a general CPU module communication port and useful for peripheral applications.
One of the leading differences between RS232 Modem and RS422/RS485 is the signaling mode. RS232 is unbalanced while RS422/RS485 is balanced. An unbalanced signal is presented by a single signal wire in which a voltage level on that one wire can be used to transmit/receive binary 1 and 0: it can be considered a push signal driver. On the other hand, a balanced signal is presented by a set of wires where a voltage difference can be used to transmit/receive binary information: kind of a push-pull signal driver. In a nutshell, unbalanced voltage level signal travels slower and shorter than the usual balanced voltage difference signal.
RS485 converter may also be termed as RS485 Multidrop LAN because it can connect several devices in a LAN network environment. These devices are linked to a single pair wire. Transmit and receive share the same two wires.
Serial to LAN bridge mode allowing transparent bridging of serial devices over LAN, while using 3 Mbps fast UART. Full Internet controller mode allows a simple microcontroller to use the module's protocol and application capabilities to do complex Internet operations for example e-mail, FTP, SSL, embedded web server and others. It also provides a firewall, providing a security gap between your application and the network. PPP modem emulation mode allows existing modem designs currently using PPP to connect transparently over LAN.
With robust metal housings and fanless cooling, the converters are claimed to provide benefits and features to match applications such as discrete manufacturing, processing operations, power generation and distribution, and building automation. Fiberstore is a leader manufacturer in serial connectivity, has introduced RS422 converter/ RS485 converter versions of their 4 and eight port Ethernet to serial products. As with all our Ethernet to Serial port devices, these new products are made to provide easy, fast and reliable connections between networked computers and devices with serial ports- be it across the desk or around the globe.
Source from Ethernet To Serial Converter Devices
Posted by: mikofy at
08:07 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 566 words, total size 5 kb.
May 20, 2013
The fiber optic connector is defined as the plug portion equipped with a tunable cylindrical ferrule while incorporating unique trigger and latch features. Better connectors lose hardly any light because of reflection or misalignment of the fibers. The LC Connector is established due to its small size and its very reliable connecting quality. Within the last five years it is the most popular connector in the world. LC means Lucent Connector also it was created by Lucent Technologies. The LC connector has good performance and it is highly favored for single-mode.
The LC Connector Product is a strong optical connector made to support Telecom and Datacom networks. The connector family includes although not restricted to Jumper Connectors, Behind the Wall connectors (BTW), Adapters, Attenuators, Jumpers and an range of connector modules and panels. LC connector applications include Telecommunications networks, Local area networks, Information systems networks, Cable television, Fiber-to-the-home, and Premises distribution.
Features of LC Connectors
Half the dimension of regular connectors;
Push & pull mechanism like RJ connectors;
Single set design;
Polarized;
Complies with industry standards;
Detachable clips for simplex in addition to duplex connectors.
LC connector utilizes traditional aspects of a SC duplex connector having independent ceramic ferrules and housings using the overall size scaled down by half. They make things easier for movements, additions, and modifications, thus preventing additional expenses. The LC Connector uses an enhanced edition of the well-known, user friendly RJ-style telephone connector that offers a reassuring clear click when connected. The latest single set design increases the connector's strength and matches side-load requirements of standard 2.5 mm connectors. Jumper LC connectors are equipped with detachable clips, making it simpler to rectify polarity inaccuracies during termination or while duplexing simplex connectors within the field.
LC connectors have replaced SC connectors in corporate networking environments due to their smaller size; they are often found on small form-factor pluggable transceivers. LC connectors reduce space requirements by 50%, over 2.50mm ferrule connectors, without having to sacrifice performance. LC connectors can be found in industry standard beige (multimode), blue (singlemode) and green (angle polish) colors, and will accommodate 900|¨¬m buffered fiber, 1.60mm, 2.00mm, or 3.00mm jacketed cable. With its six-position tuning feature, the connector enables you to achieve unprecedented insertion loss performance by optimizing the alignment from the fiber cores. Additionally, 45° and 90° boot choices are available for 1.60mm and a pair of.00mm jacketed cable.
As you may know, fiber optic connector is a vital fiber optic component used to link two fiber optic lines together. Beside connector, addititionally there is another item, that is Fiber optic adapter with panels to connecting multi fiber optic line. Specifically, the fiber optic adapter is a small device that accustomed to terminate or link the fiber optic cables or fiber optic connectors between two fiber optic lines.
A fiber optic connector terminates at the end of a fiber optic cable and is used when you need a way to connect and disconnect the fiber cable quickly. A fiber splice would be utilized in a more permanent application. The connectors give a mechanical connection for the two fiber cables and align both cores precisely so the light can go through with little loss. LC connectors look much like miniature SC connectors. LC connector also offers exactly the same push/pull snap-in type secure. The distinctive combination of small sizes and also the click of connectivity result in the LC Connector an ideal pick for today's high performance networks.
Source from The Most Popular LC Connector
Posted by: mikofy at
08:24 AM
| No Comments
| Add Comment
Post contains 587 words, total size 5 kb.
30 queries taking 0.126 seconds, 89 records returned.
Powered by Minx 1.1.6c-pink.